FieldsStatistical physics and thermodynamics
-
NEW
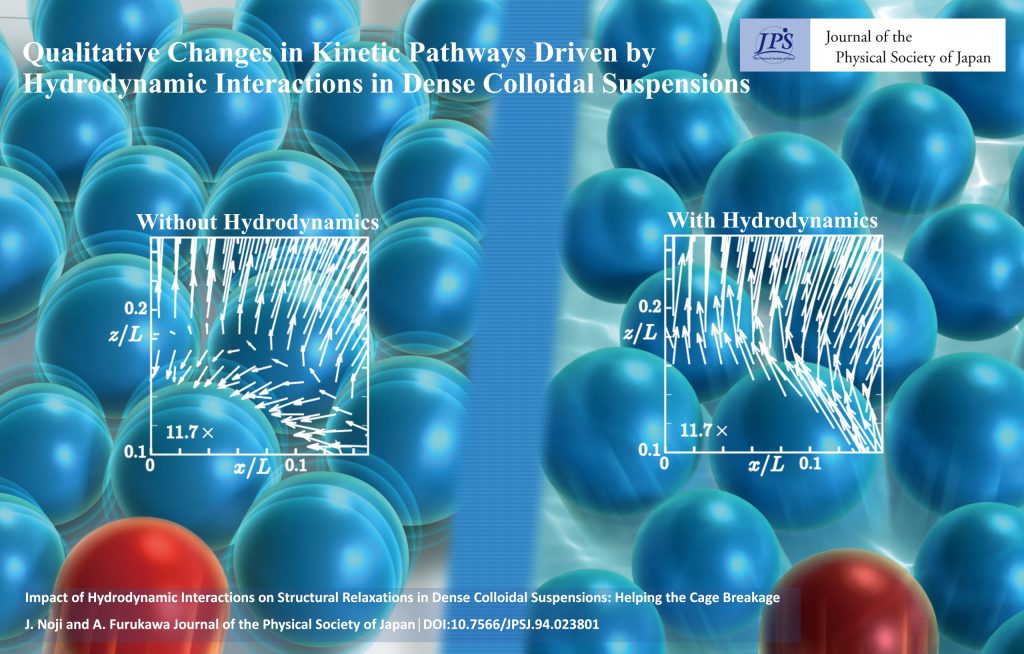 Qualitative Changes in Kinetic Pathways Driven by Hydrodynamic Interactions in Dense Colloidal Suspensions
Qualitative Changes in Kinetic Pathways Driven by Hydrodynamic Interactions in Dense Colloidal Suspensions2025-4-18
Even in dense colloidal suspensions, where long-range hydrodynamic interactions are screened, near-field hydrodynamic interactions qualitatively influence the selection of kinetic pathways.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
-
PICKUP
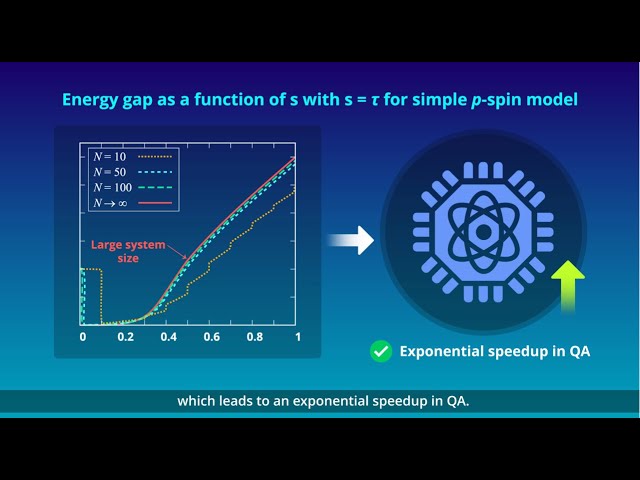 Overcoming Phase Transitions for Faster Quantum Annealing
Overcoming Phase Transitions for Faster Quantum Annealing2025-3-27
This study presents an innovative method to address the problem of phase transitions in quantum annealing, resulting in an exponential speedup of the process.
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
PICKUP
 Exploring the Vibrant Interplay of Machine Learning and Physics
Exploring the Vibrant Interplay of Machine Learning and Physics2025-3-13
This Journal of the Physical Society of Japan Special Topics edition explores how physics and machine learning complement each other and can solve unresolved problems in physics.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Electron states in condensed matter
Elementary particles, fields, and strings
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Superconductivity
-
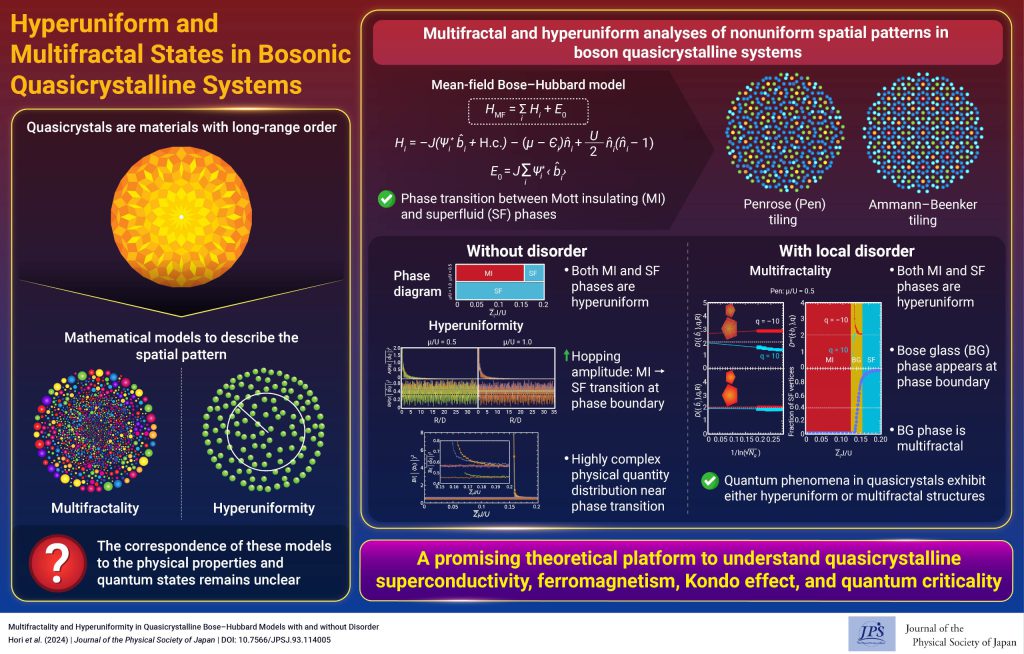 Hyperuniform and Multifractal States in Bosonic Quasicrystalline Systems
Hyperuniform and Multifractal States in Bosonic Quasicrystalline Systems2025-2-10
Quantum states can be categorized as hyperuniform or multifractal based on electronic characteristics. This study demonstrates that bosonic quasicrystalline systems exhibit hyperuniform or multifractal quantum states.
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
-
 A Neural Thermometer for Predicting Phase Transitions of Unknown Systems
A Neural Thermometer for Predicting Phase Transitions of Unknown Systems2024-9-11
A novel convolutional neural network predicts phase transition temperatures from spin configurations without prior information about order parameters, paving the way for the discovery of new materials in condensed matter physics.
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
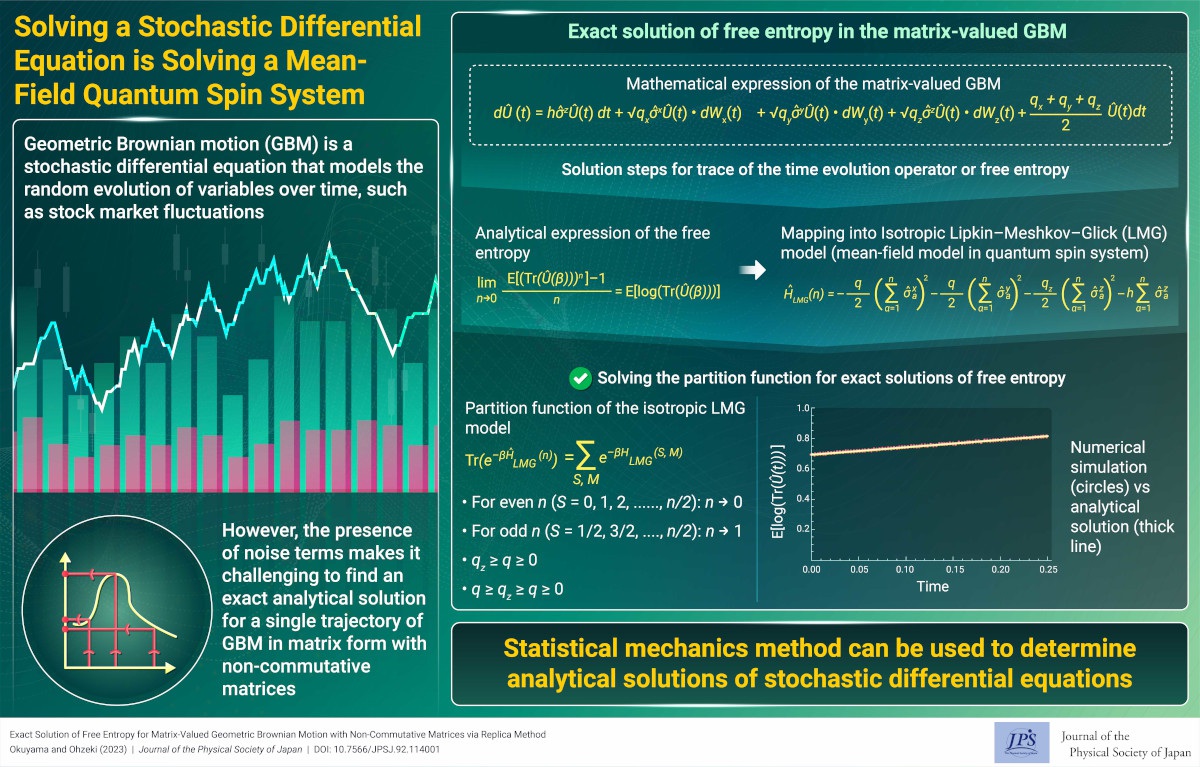 Solving a Stochastic Differential Equation is Solving a Mean-Field Quantum Spin System
Solving a Stochastic Differential Equation is Solving a Mean-Field Quantum Spin System2024-5-16
The replica method maps matrix-valued geometric Brownian motion to a mean-field quantum spin system. This correspondence makes it possible to obtain an exact solution for matrix-valued geometric Brownian motion.
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
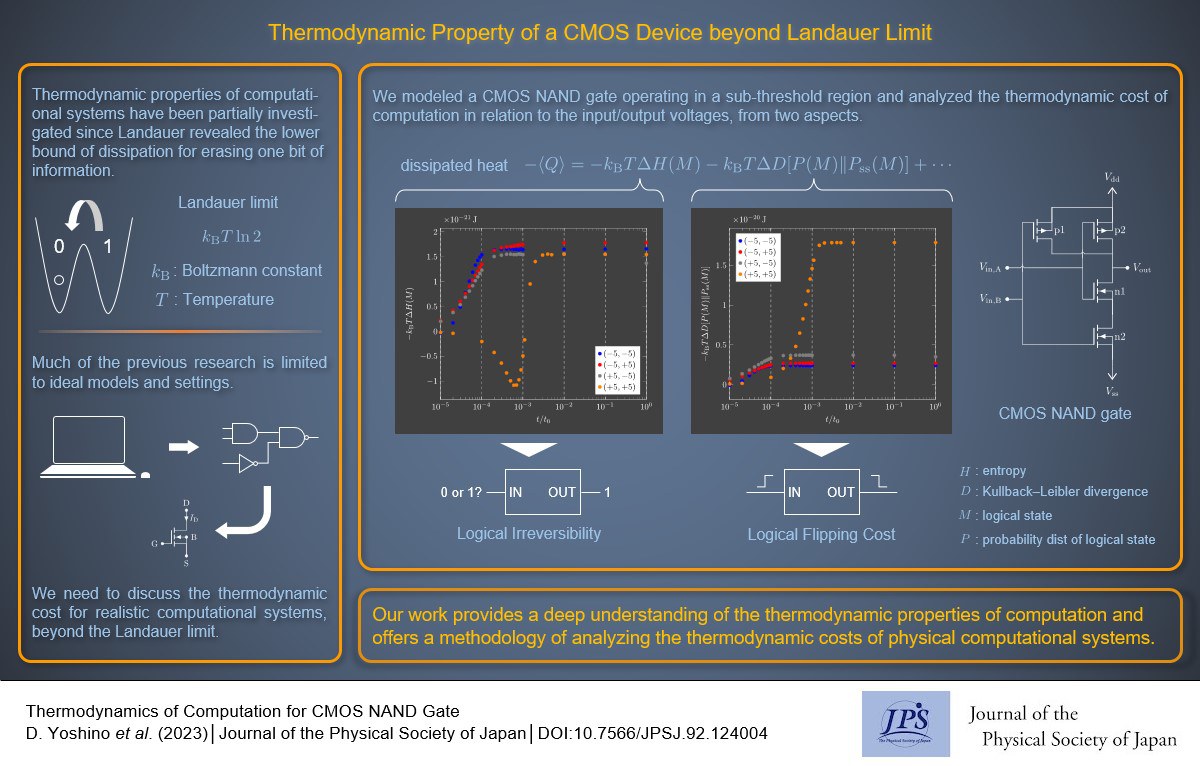 Thermodynamic Property of a CMOS Device beyond Landauer Limit
Thermodynamic Property of a CMOS Device beyond Landauer Limit2024-1-23
Focusing on a CMOS NAND GATE operating in a sub-threshold region, the thermodynamic cost of computation was analyzed in relation to input/output voltages surpassing the Landauer limit.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
PICKUP
 Exploring Recent Advances in the Physics of Biofluid Locomotion
Exploring Recent Advances in the Physics of Biofluid Locomotion2023-12-8
This Special Topics Edition of the JPSJ describes the latest advances in the field of biofluid locomotion, shedding light on the underlying physics behind the movement of organisms that swim and fly.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Electromagnetism, optics, acoustics, heat transfer, and classical and fluid mechanics
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
-
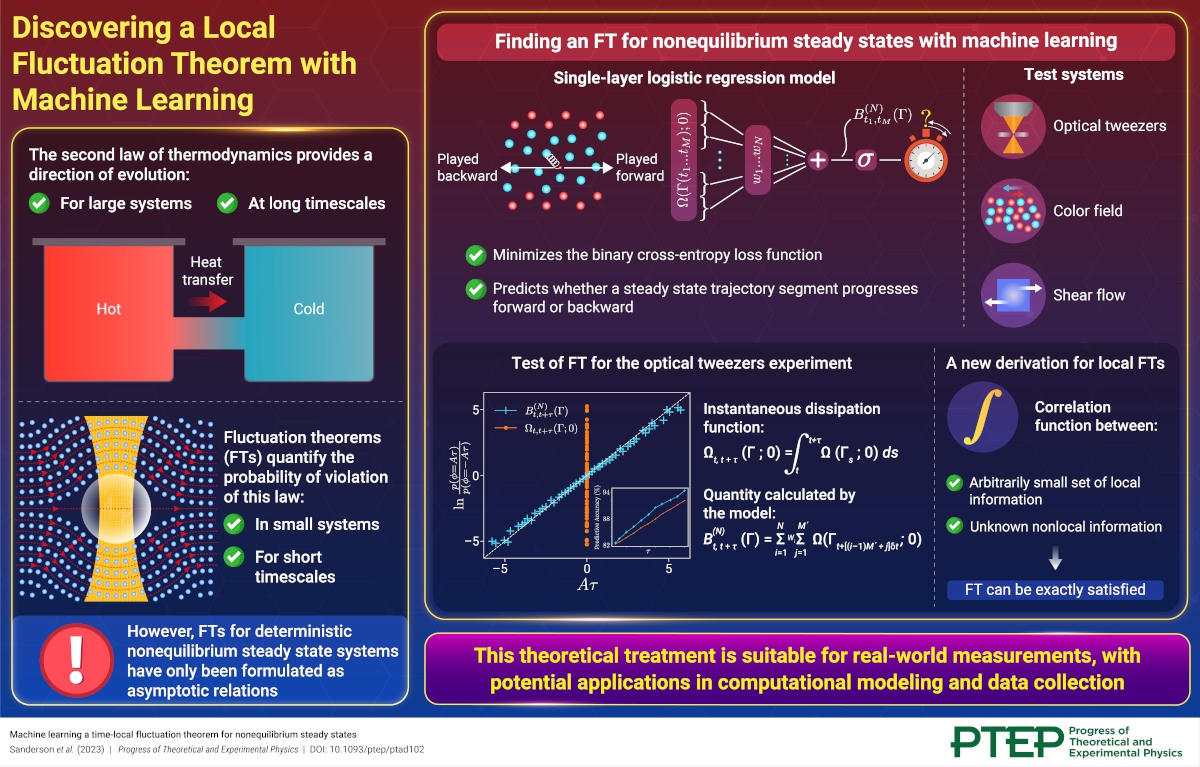 Discovering a Local Fluctuation Theorem with Machine Learning
Discovering a Local Fluctuation Theorem with Machine Learning2023-10-20
A groundbreaking study reveals a new time-local fluctuation theorem using machine learning, revolutionizing our understanding of deterministic nonequilibrium steady state systems.
Fundamental Theory of Condensed Matter Physics, Statistical Mechanics, Fluid Dynamics,
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
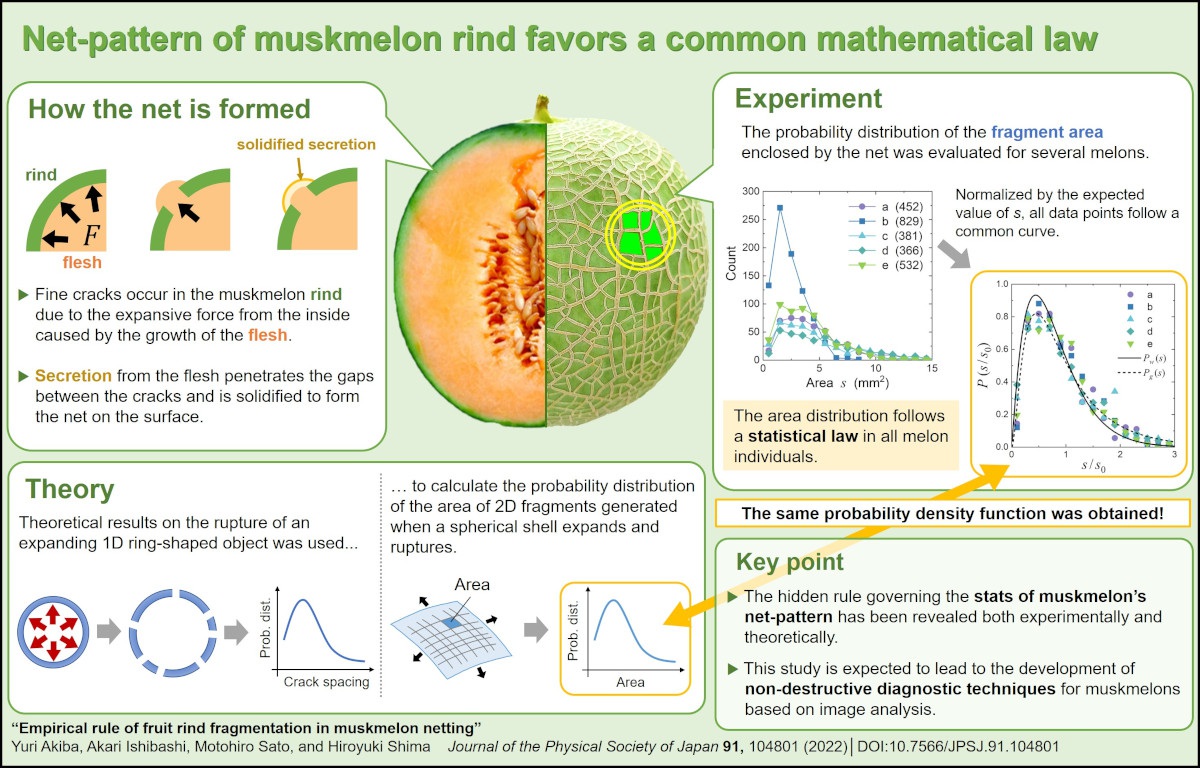
Net-Pattern of Muskmelon Rind Favors a Common Mathematical Law
2023-1-12
The surface of muskmelon is covered with a fine mesh-like net-pattern. The geometric features of the fine mesh appear unique for each individual, but hide an unexpected mathematical rule.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
PICKUP
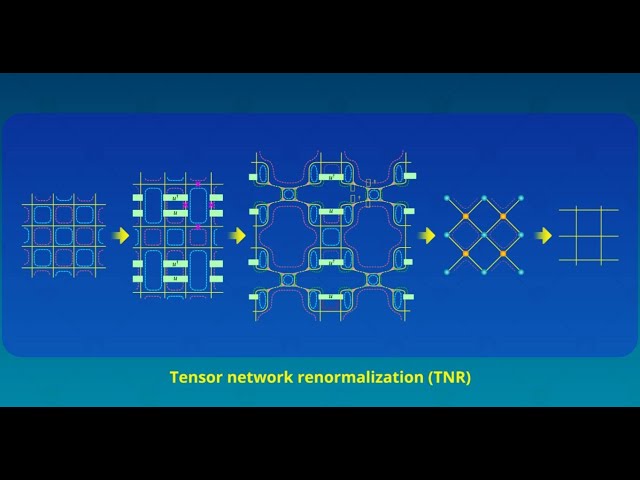 Tensor Networks Across Physics
Tensor Networks Across Physics2022-6-7
Researchers from Japan provide the first comprehensive review of the historical development of tensor networks from a statistical mechanics viewpoint, with a focus on its theoretical background.
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
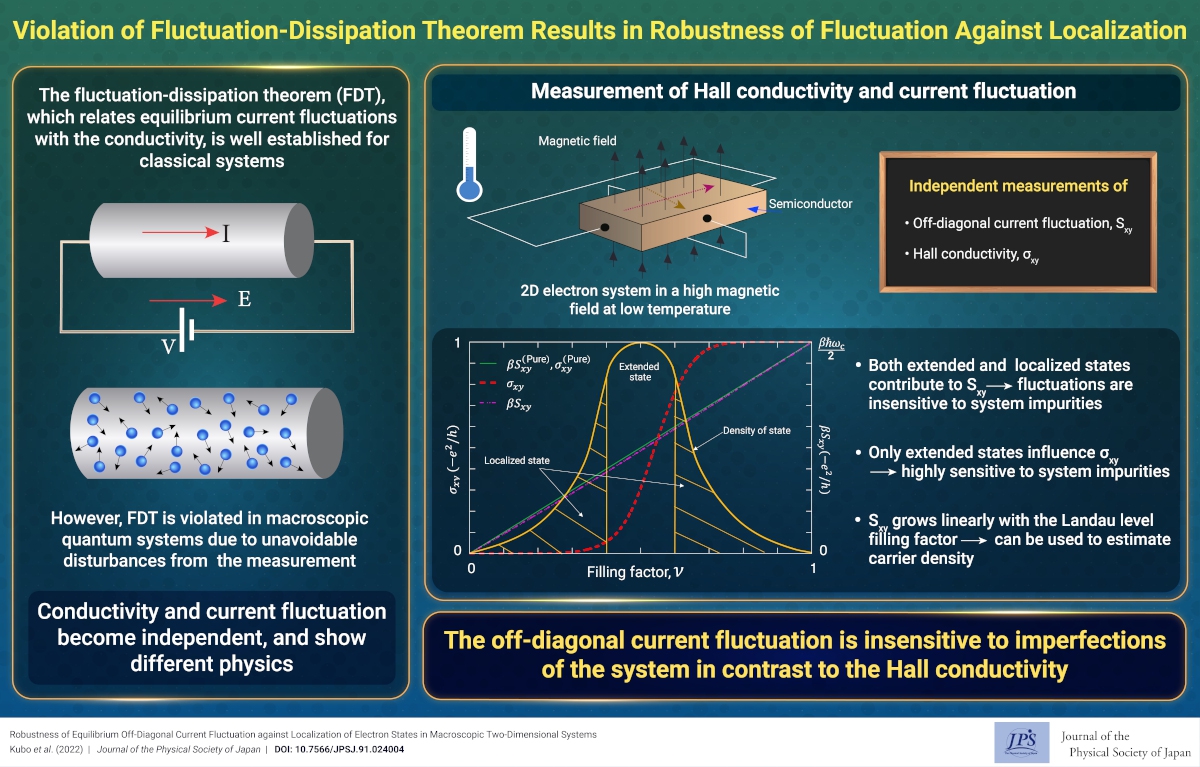 Violation of Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem Results in Robustness of Fluctuation Against Localization
Violation of Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem Results in Robustness of Fluctuation Against Localization2022-3-23
We study equilibrium current fluctuations in systems without time-reversal symmetry, violating the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Notably, the off-diagonal fluctuation is insensitive to system imperfections in contrast to other fluctuations and conductivity.
Electronic structure and electrical properties of surfaces and nanostructures
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
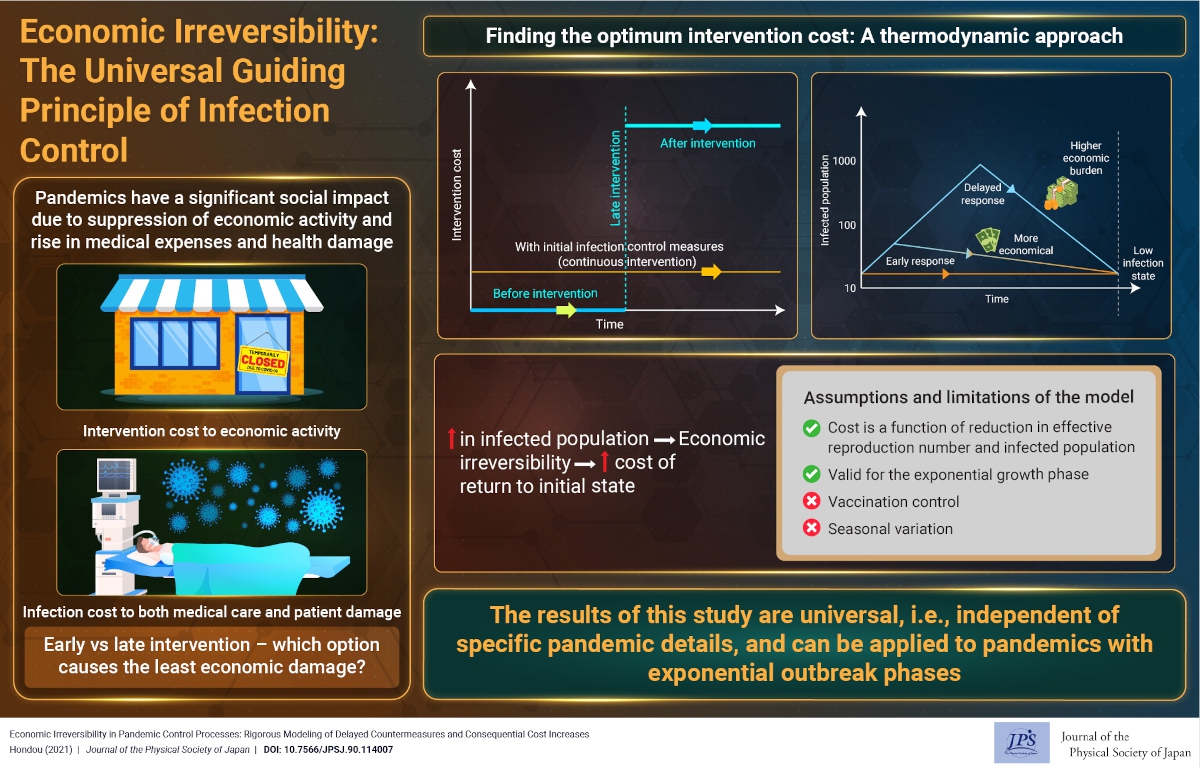 Economic Irreversibility: The Universal Guiding Principle of Infection Control
Economic Irreversibility: The Universal Guiding Principle of Infection Control2022-3-1
It is preferable to avoid lockdowns, as lockdowns at seriously spread phases are very expensive. It would be economically better to utilize less intense countermeasures as early as possible to avoid lockdowns in later phases.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
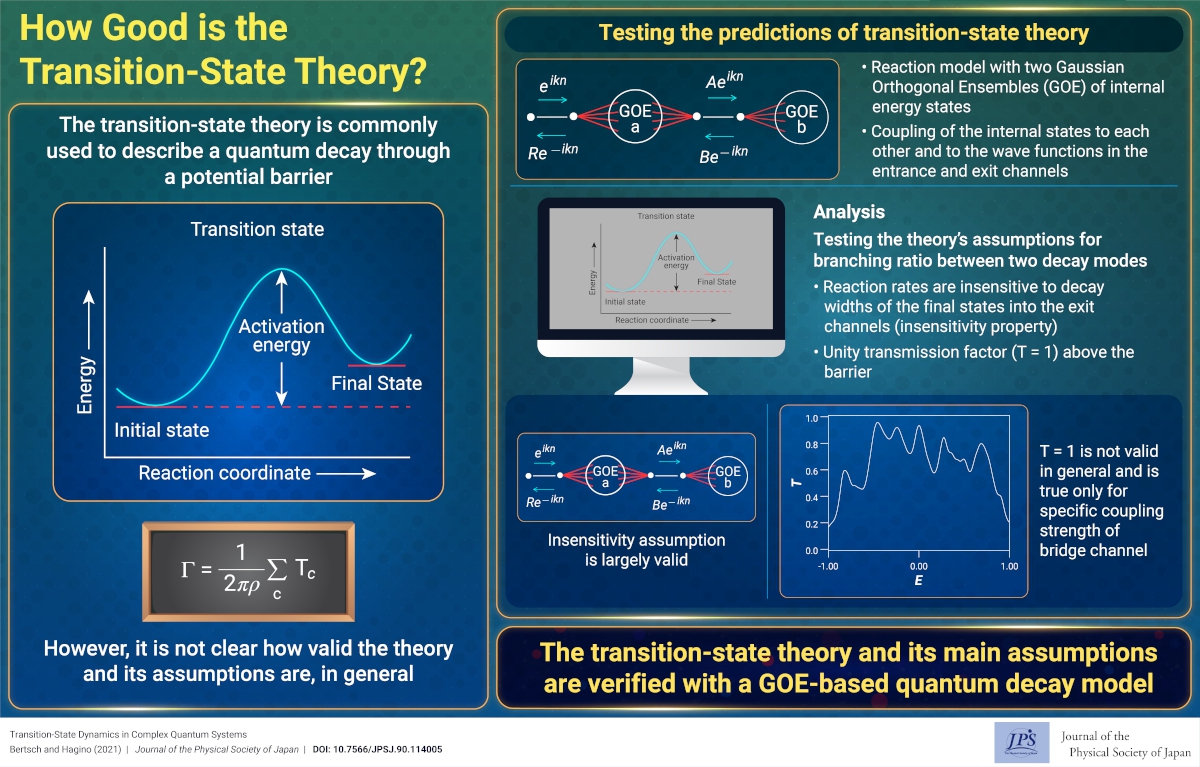 How Good is the Transition-State Theory?
How Good is the Transition-State Theory?2021-11-30
For the first time, the main assumption of the transition-state theory for the decay of complex quantum systems across a potential barrier was realized using a microscopic many-body Hamiltonian.
Nuclear physics
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
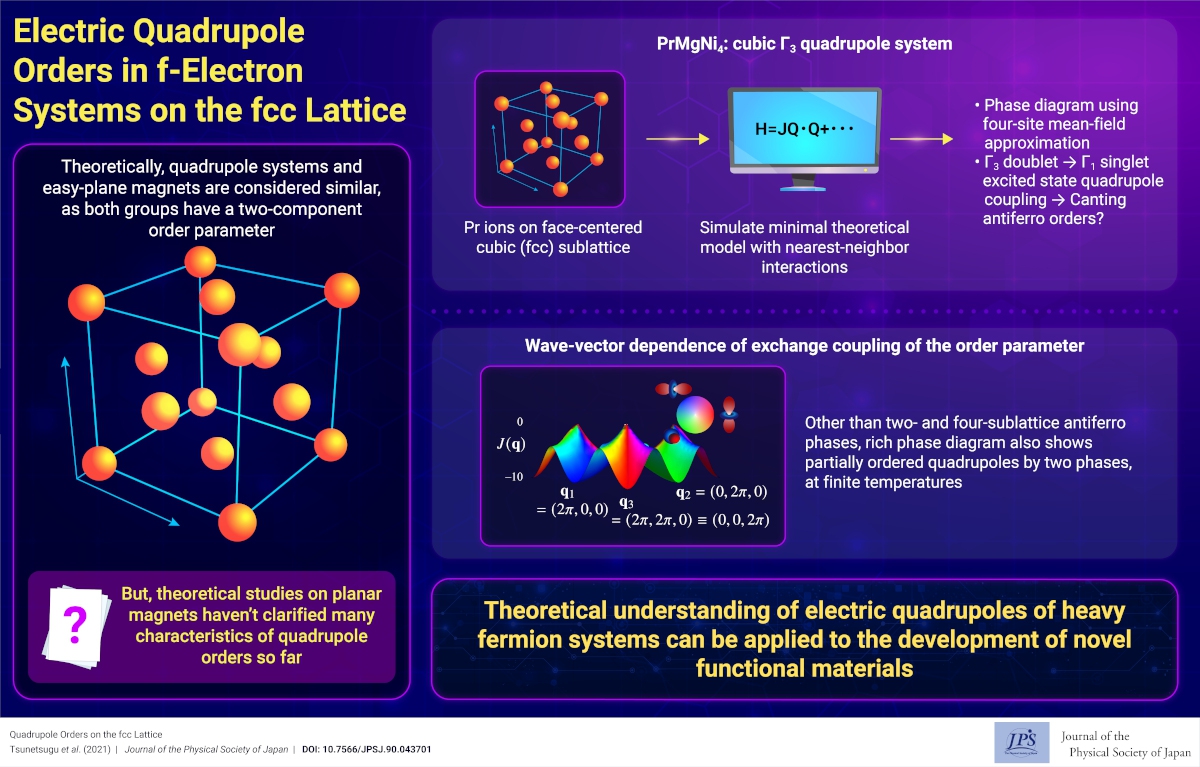 Electric Quadrupole Orders in f-Electron Systems on the fcc Lattice
Electric Quadrupole Orders in f-Electron Systems on the fcc Lattice2021-5-17
We theoretically showed that electric quadrupoles in some heavy fermion materials exhibit a very rich phase diagram including unique partially-ordered phases stabilized by an interaction specific to these systems.
Dielectric, optical, and other properties in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
Electronic Nematic Ordering Driven by Atomic-scale Multipoles
2021-5-13
Theoretical investigations have unearthed a plethora of electronic nematic orderings driven by the spatial distribution of atomic-scale electric quadrupoles.Dielectric, optical, and other properties in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
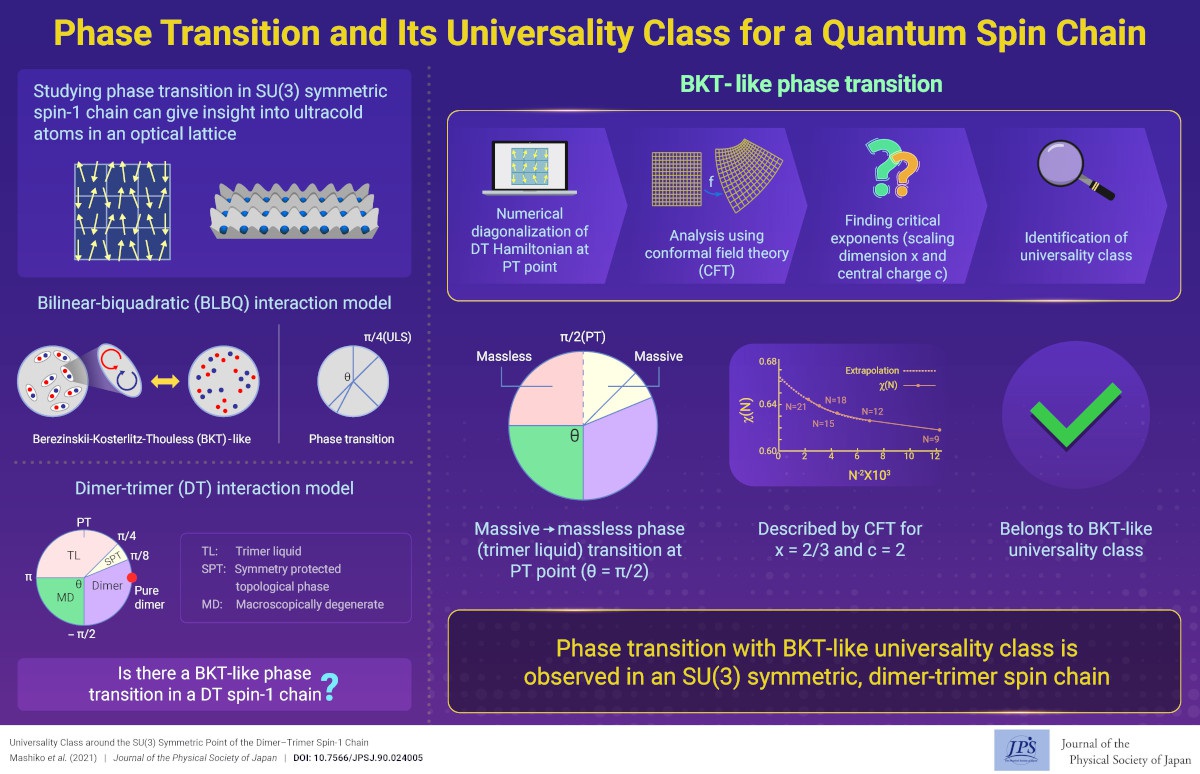 Phase Transition and Its Universality Class for a Quantum Spin Chain
Phase Transition and Its Universality Class for a Quantum Spin Chain2021-3-29
We numerically diagonalize the Dimer-Trimer (DT) model Hamiltonian around the SU(3) symmetric point. As a result, we discover the phase transition at this point which belongs to the Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless (BKT)-like universality class.
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
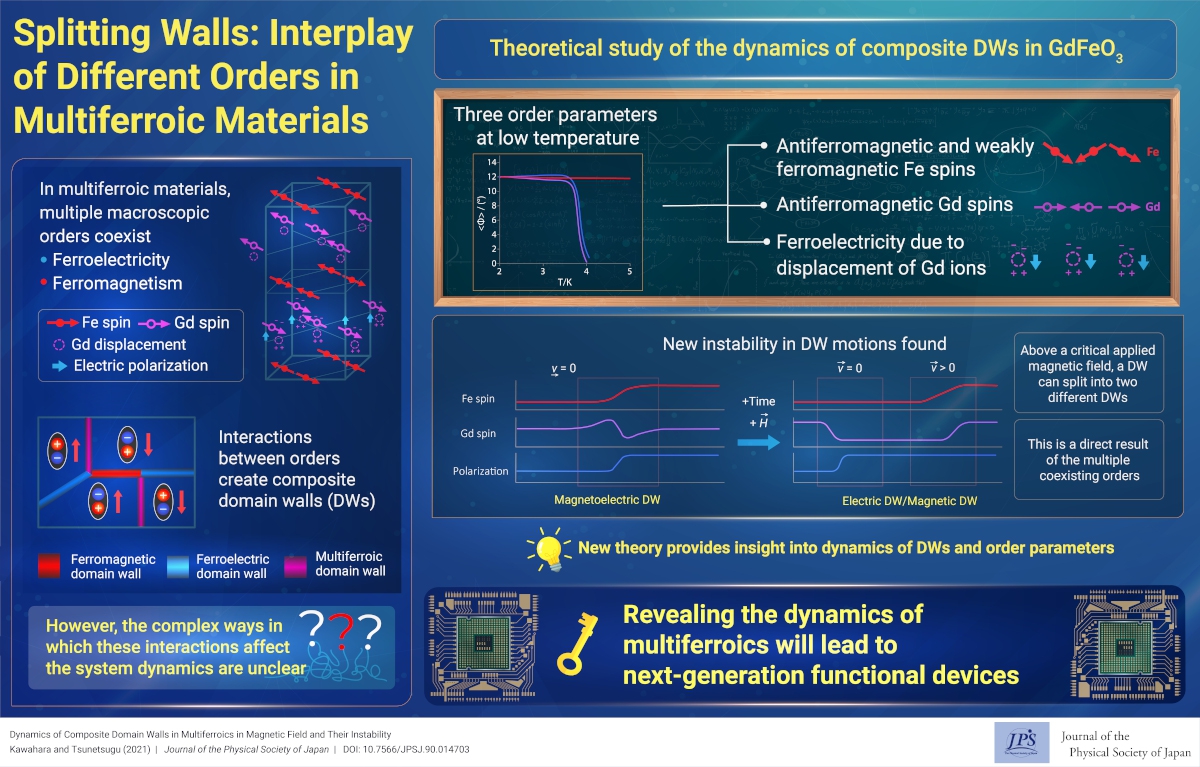
Splitting Walls: Interplay of Different Orders in Multiferroic Materials
2021-3-29
We theoretically showed an intrinsic splitting instability of composite domain walls in multiferroic materials under field drive. This instability is a direct result of the coexistence of multiple orders in the system.
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
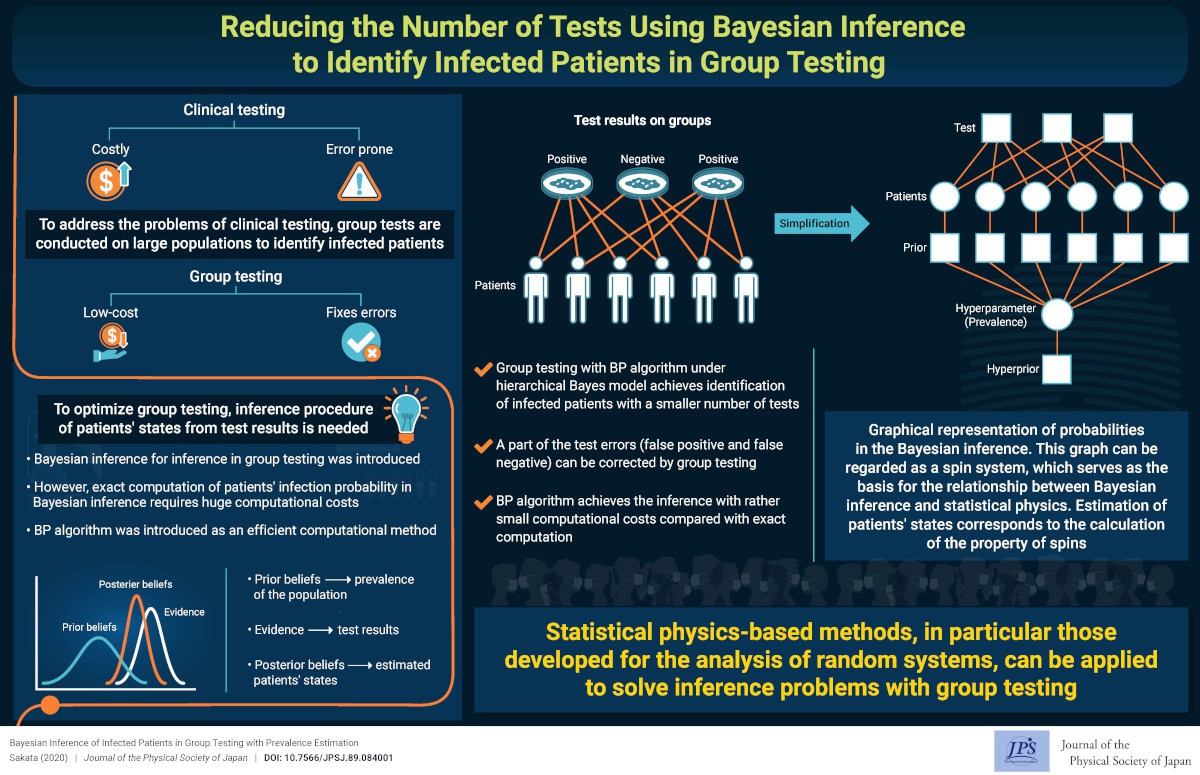
Reducing the Number of Tests Using Bayesian Inference to Identify Infected Patients in Group Testing
2021-3-22
Group testing is a method of identifying infected patients by performing tests on a pool of specimens. Bayesian inference and a corresponding belief propagation (BP) algorithm are introduced to identify the infected patients in group testing.
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-

How is Brownian Motion Affected by a Fluctuating Random Surface?
2021-3-15
A researcher has developed a new theory to describe the Brownian motion of a small object that is confined in a fluctuating random surface.
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
-
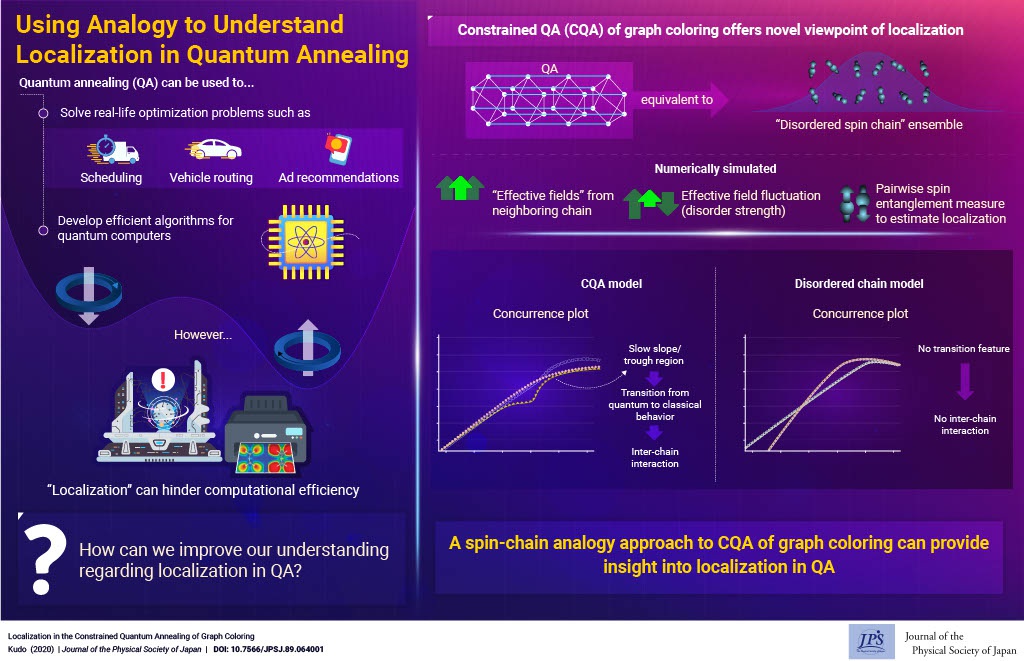
Using Analogy to Understand Localization in Quantum Annealing
2021-3-15
Localization may cause the inefficiency of quantum annealing. The constrained quantum annealing of graph coloring provides a new viewpoint to analyze localization phenomena in quantum annealing.
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
 Multiple Superconducting Phases in UTe2: A Complex Analogy to Superfluid Phases of 3He
Multiple Superconducting Phases in UTe2: A Complex Analogy to Superfluid Phases of 3He2021-3-3
In quantum liquids, large differences are observed owing to differences in quantum statistics. The physical properties of liquid 3He (Fermion) and 4He (Boson) are considerably different at low temperatures. After the discovery of superconductivity in electron (i.e., Fermion) systems, a similar pairing ordered state was expected for 3He. Remarkably, the observed ordered state of 3He was more surprising than expected, multiple superfluid phases in the T–P phase diagram. The origin of the multiple phases was attributed to ferromagnetic interactions in the p-wave symmetry state.
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
-
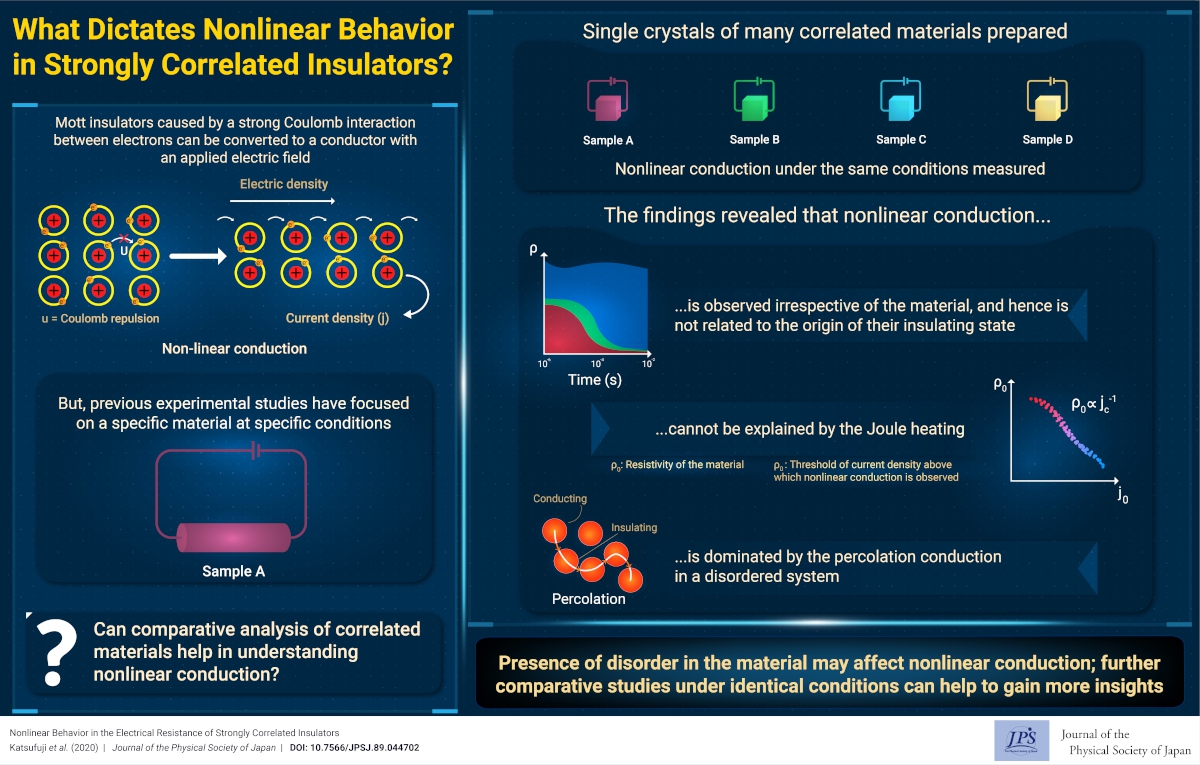 What Dictates Nonlinear Behavior in Strongly Correlated Insulators?
What Dictates Nonlinear Behavior in Strongly Correlated Insulators?2021-3-3
The nonlinear conduction (the deviation from Ohm's law) has been discovered universally in various correlated materials. This may be explained by the percolation conduction in disordered materials.Electronic transport in condensed matter
Statistical physics and thermodynamics

