Understanding Relaxor Ferroelectrics with Simple Landau Theory
© The Physical Society of Japan
This article is on
Nonlinear Dielectric Susceptibility in Pb(Sc1/2Ta1/2)O3 Single Crystals
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 91, 054702 (2022).
Third-order nonlinear dielectric susceptibility is measured in the paraelectric phase of Pb(Sc1/2Ta1/2)O3. The linear and nonlinear dielectric susceptibility results can be consistently explained based on the Landau-type free-energy density.
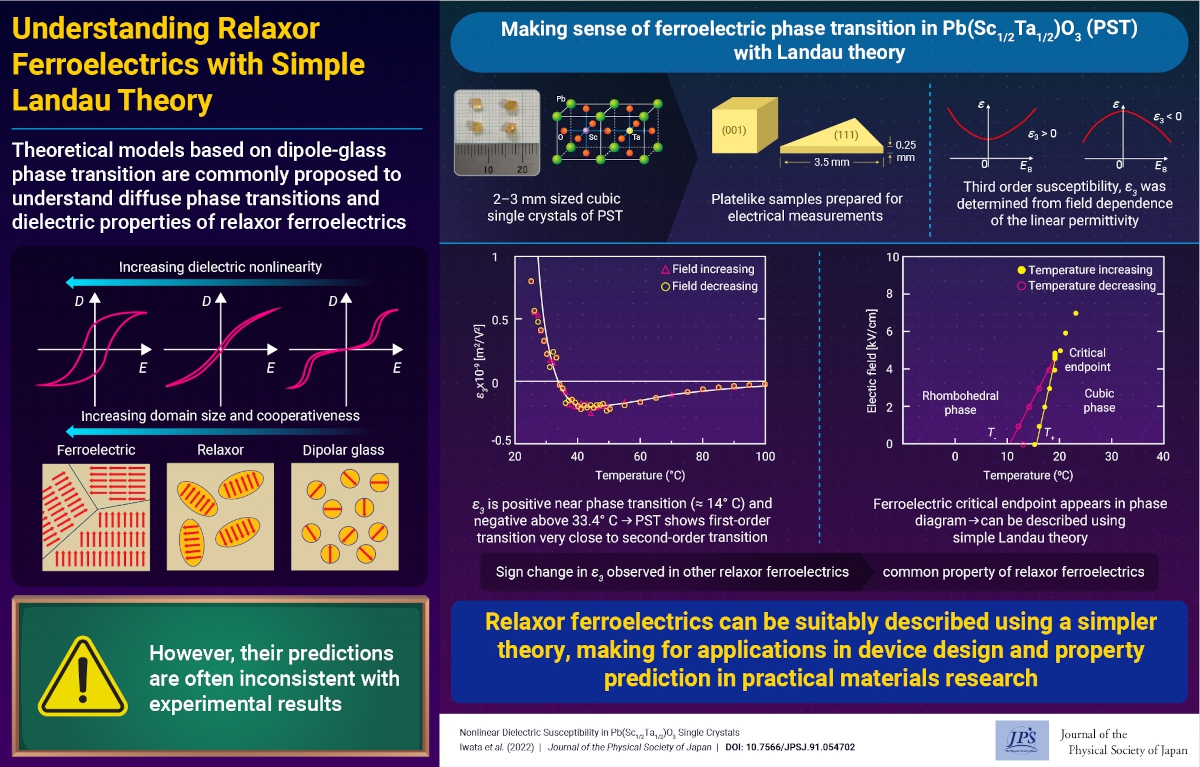
Pb(Sc1/2Ta1/2)O3 (PST) is a perovskite-type ferroelectric oxide that exhibits relaxor-like characteristics. A relaxor is a material that exhibits a diffuse phase transition with a wideband dispersion in dielectric permittivity over many orders of magnitude. One of the most challenging issues in the physics of ferroelectrics is to understand the inherent dielectric properties of relaxor ferroelectrics.
To explain the physical properties of relaxors, many theoretical models based on the dipolar-glass transition have been proposed wherein the third-order nonlinear dielectric susceptibility e3 was theoretically predicted to indicate a negative divergence at the dipolar-glass transition temperature. However, it has been reported that in some relaxor ferroelectrics, the measured e3 takes positive values without any indication of divergence near the temperature Tm at which the linear permittivity is maximum. This is inconsistent with the predictions made by the theoretical models based on the dipolar-glass phase transition. Therefore, to explain the temperature dependence of e3, a new model is required. The ferroelectric critical endpoint (CEP) in the temperature–field phase diagram in many perovskite relaxor ferroelectrics has been extensively investigated. The PST temperature–field phase diagram has been obtained, and the existence of ferroelectric CEP was demonstrated. The appearance of the ferroelectric CEP in relaxors implies that relaxor ferroelectrics can be investigated based on the simple Landau-type free-energy density, similar to a conventional ferroelectric material, without any complex models based on dipolar-glass phases. Under these circumstances, in the present study, the linear and nonlinear dielectric susceptibilities in the paraelectric phase of PST were measured. The results were explained based on the Landau-type free-energy density.
The experimental results reveal that e3 takes a positive value near Tm (approximately 14 °C) and becomes negative above T1 = 33.4 °C. It was concluded that the positive e3 near Tm in PST results from the first-order transition because the sign of b (coefficient of the fourth-order term of the polarization in the Landau-type free-energy density) directly depends on the sign of e3. Furthermore, a change in the sign of e3 near the transition temperature in PST indicates that b is relatively small, thereby implying that the phase transition in PST is close to the second-order transition. Such a change in the sign of e3 in paraelectric phase has been reported for several perovskite-type ferroelectrics, such as BaTi1–xZrxO3, PZN–PT, and PMN–PT, which indicates that it might be a property common to many perovskite ferroelectrics.
In this study, the relationship between the third-order susceptibility e3 and ferroelectric phase transition in PST was clarified based on macroscopic thermodynamics.
(written by M. Iwata on behalf of all authors)
Nonlinear Dielectric Susceptibility in Pb(Sc1/2Ta1/2)O3 Single Crystals
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 91, 054702 (2022).
Share this topic
Fields
Related Articles
-
d2 Trimer and d3 Tetramer in a Pyrochlore Lattice
Dielectric, optical, and other properties in condensed matter
Electron states in condensed matter
2024-7-11
Based on the charge disproportionation of V3+ and V2+, the V3+(d2) trimers and V2+(d3) tetramers in the vanadium pyrochlore lattice of AlV2O4 are described by the orbitally-induced Peierls mechanism.
-
Structural Rotation and Falsely Chiral Antiferromagnetism: A New Combination Generating Ferrotoroidic State
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Dielectric, optical, and other properties in condensed matter
2024-7-4
The ferrotoroidic state, an exotic state of matter with broken space inversion and time-reversal symmetries, was achieved by combining structural rotation and falsely chiral antiferromagnetism in PbMn2Ni6Te3O18.
-
Evaluation of the Exchange Stiffness Constants of Itinerant Magnets from the First-Principles Calculations
Electron states in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-6-5
Using first-principles calculations, we evaluated the exchange stiffness constants of ferromagnetic metals at finite temperatures. The constants can be used as parameters in the Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation.
-
Which is Moving?—Pinning Down the Origin of Fluctuations in Muon Spin Relaxation—
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
2024-3-28
The study demonstrated that we can distinguish between the diffusion motion of the muon itself and the motion of the surrounding ions in muon spin relaxation.
-
Variety of Mechanically Induced Spin Currents in Rashba Systems
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-3-22
Various types of spin currents, including unconventional types, are generated in Rashba spin-orbit coupled systems by dynamic lattice distortions associated with, for example, surface acoustic waves.
