Study of Unconventional Slow Critical Dynamics of the Frustrated Magnet DyRu2Si2 ~Spontaneous Alignment of Emergent Ferromagnetic Spin Textures?~
© The Physical Society of Japan
This article is on
Novel Slow Dynamics of Phase Transition in the Partially Ordered Frustrated Magnet DyRu2Si2
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 92, 094705 (2023).
We measured the ac susceptibility of the frustrated magnet DyRu2Si2, in the partially ordered phase, where emergent 2-dimensional (2-D) disordered planes appear, and revealed extraordinarily slow and unconventional dynamics, which could be attributed to the highly fluctuating nature of the emergent 2-D planes.
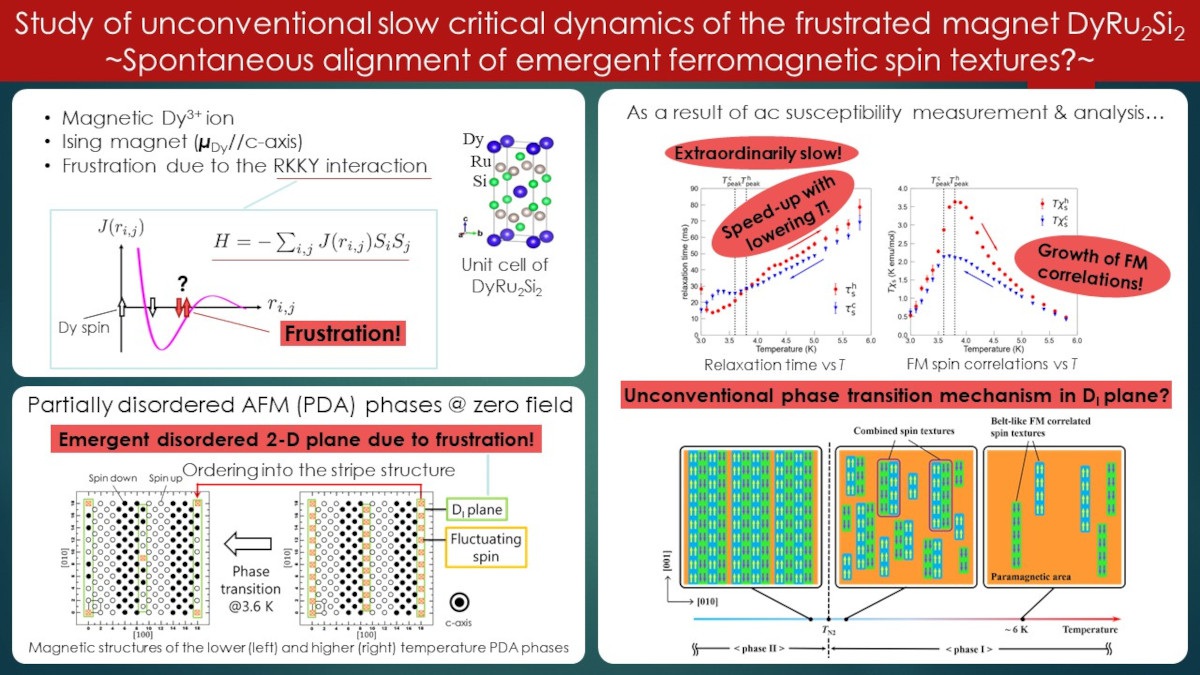
Magnetic frustration due to the competition between magnetic interactions is a promising stage for the discovery of novel phenomena in magnets. Under magnetic frustration, many different spin configurations can have nearly the same energy in a system, and thus, the ground state can degenerate magnificently, such as in the case of spin ice and spin glass. Among them, slow dynamics on the order of ms to µs can be observed, which is 6 to 9 orders of magnitude slower than the ordinary dynamics in non-frustrated magnets.
This study focuses on such extraordinarily slow dynamics in the vicinity of the phase transition at zero magnetic field in the frustrated magnet DyRu2Si2, where the oscillating RKKY interaction between Dy3+ spins causes frustration. At zero field, DyRu2Si2 exhibits multi-step phase transitions. One atTN1 = 29.5 K, from the paramagnetic phase to the phase I, and the other at TN2 = 3.6 K, from the phase I to II. The phase I and II are partially disordered antiferromagnetic (AFM) phases, where disordered and fluctuating spins remain. This is an outcome of the frustration effect, namely the cancel-out of interactions at specific spin sites. In the phase I, disordered a-planes (DI planes) on which all spins fluctuate appear every 9 planes. The DI-planes are decoupled from each other because the interactions from the ordered a-planes in between are canceled out. Therefore, the DI planes are identified as emergent pseudo 2-dimensional (2-D) systems. In the phase II, these fluctuating spins on the DI planes order into a stripe structure. Hence, the I-II phase transition in DyRu2Si2 can be considered as spin-ordering in the emergent 2-D systems.
We conducted detailed ac susceptibility measurements around TN2 and revealed the strikingly anomalous dynamics attributed to the I-II phase transition as follows: ① the extraordinarily slow dynamics in the order of 10-100 ms appears around 6 K far above TN2, ② the relaxation time reduces as temperature decreasing, indicating non-thermally activated origin, ③ the critical slowing down is absent at TN2, and ④ the ferromagnetic (FM) spin correlations grow toward TN2, even though it is an AFM phase transition.
On the basis of these findings, we propose a schematic of the I-II phase transition. Prior to the phase transition, large belt-like FM spin textures extending along c-axis emerge as precursors of the striped structure of the phase II. As approaching TN2, they grow in size and number and couple antiparallel to each other. Finally, at TN2, they spontaneously order into the striped structure. This anomalous ordering process to the phase II could be the highly fluctuating nature of the emergent 2-D systems.
Written by S. Yoshimoto on behalf of all the authors.
Novel Slow Dynamics of Phase Transition in the Partially Ordered Frustrated Magnet DyRu2Si2
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 92, 094705 (2023).
Share this topic
Fields
Related Articles
-
Exploring Electronic States in BEDT-TTF Organic Superconductors
Superconductivity
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
2024-4-24
This review, published in the Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, provides a comprehensive summary of the electronic states observed in BEDT-TTF type organic superconductors, including metal-insulator transitions, Mottness transitions, non-Fermi liquids, quantum spin liquids, and Bose-Einstein condensation.
-
Variety of Mechanically Induced Spin Currents in Rashba Systems
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-3-22
Various types of spin currents, including unconventional types, are generated in Rashba spin-orbit coupled systems by dynamic lattice distortions associated with, for example, surface acoustic waves.
-
Current Melt Frozen Electrons
Dielectric, optical, and other properties in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
2024-1-15
The origin of the current-induced insulator-to-metal transition of samarium monosulfide was explained by the 4f−5d hybridization observed using optical reflectivity and photoelectron spectroscopies.
-
Towards Uncovering the Hidden Order of URu2Si2 Phase Transition
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Electronic structure and electrical properties of surfaces and nanostructures
2024-1-11
We propose a chiral charge as the hidden order parameter in URu2Si2 and present experiments to detect it by focusing on breakings of mirror and inversion symmetries at the local uranium ion.
-
Magnetic Excitation in S = 1/2 Antiferromagnetic Chain CsCoCl3 with Ising-Like Exchange Interaction
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
2023-11-13
The results of high-field electron spin resonance measurements in the millimeter-wave to terahertz region reveal unconventional magnetic excitation in S = 1/2 one-dimensional antiferromagnets.
