How Good is the Transition-State Theory?
© The Physical Society of Japan
This article is on
Transition-State Dynamics in Complex Quantum Systems
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 114005 (2021).
For the first time, the main assumption of the transition-state theory for the decay of complex quantum systems across a potential barrier was realized using a microscopic many-body Hamiltonian.
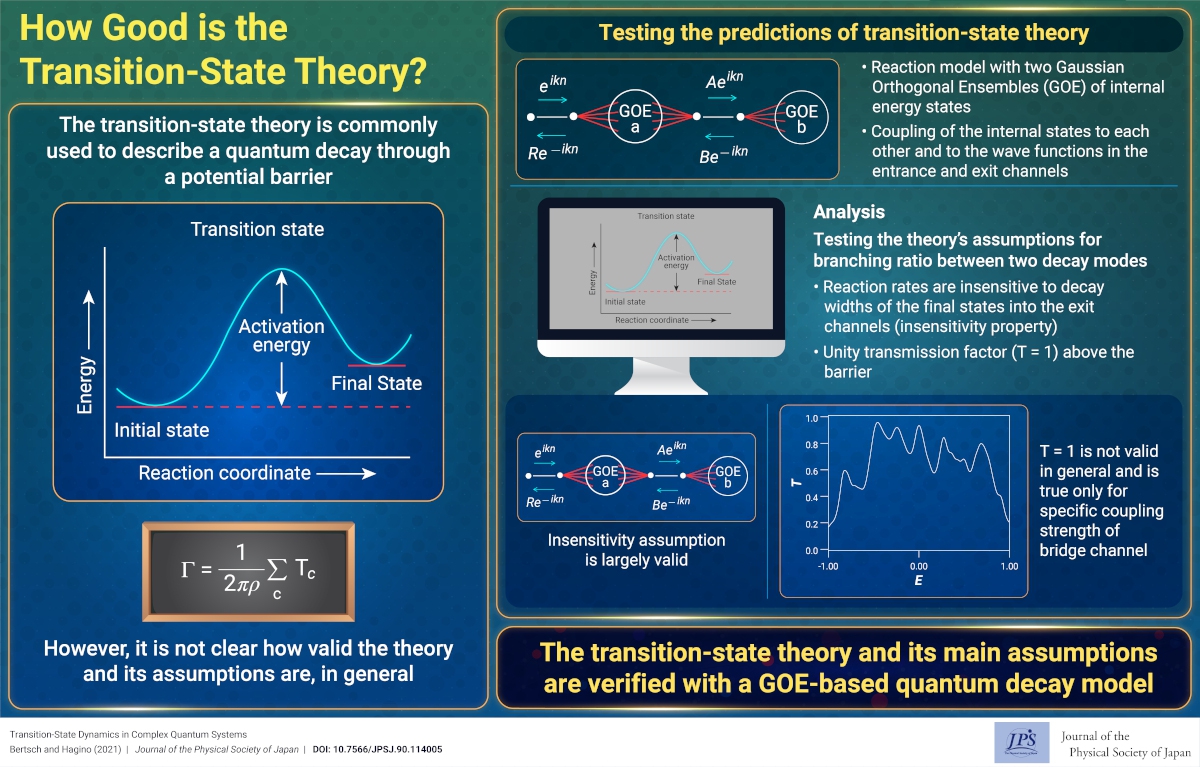
The decay of quantum systems through a potential barrier is ubiquitous in many fields of physics and chemistry, occurring in electron conduction within devices and quantum dots as well as chemical reactions, and nuclear fission. The usual framework for describing the barrier crossing is the "transition-state" theory, which was invented long ago to investigate chemical reactions and nuclear fission. The main assumption of this theory is that the decay rate is entirely determined at the highest point of the barrier and does not depend on what occurs afterward. This remarkable theory has been part of reaction theory since the 1930s and has been used in disciplines as widely distinct as chemistry and nuclear physics. However, this theory has not been validated for the quantum mechanics of many interacting particles.
In this study, a model was proposed to study reactions in systems with many interacting particles. The model allowed us to test whether the assumptions of the transition state theory could be satisfied in a full quantum theory. The model contains two reservoirs of internal states connected to each other by additional barrier-top states, and the reservoir states were considered using random matrix theory.
For the first time, we demonstrated that a main assumption of the transition-state theory can be easily satisfied by a more detailed theory, that is, the overall decay rate going through the far-side reservoir is largely determined by the barrier region and internal properties of the reservoirs, and is insensitive to the individual decay rates of the states out of the far-side reservoir.
In a subsequent paper (K. Hagino and G.F. Bertsch, Phys. Rev. E104, L052104(2021)), we applied the same model to discuss the variation of the decay rates between states. There is a well-established theory known as the Porter-Thomas distribution that has been validated for many systems, including atomic spectra, chemical reaction spectra, and nuclei. Surprisingly, our transition-state model revealed that this distribution differed depending on how large the individual rates were. The new distribution followed a different random matrix model, namely the Gaussian Unitary Ensemble, proposed by Dyson in 1960.
(Written by K. Hagino on behalf of all authors)
Transition-State Dynamics in Complex Quantum Systems
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 114005 (2021).
Share this topic
Fields
Related Articles
-
Solving a Stochastic Differential Equation is Solving a Mean-Field Quantum Spin System
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
2024-5-16
The replica method maps matrix-valued geometric Brownian motion to a mean-field quantum spin system. This correspondence makes it possible to obtain an exact solution for matrix-valued geometric Brownian motion.
-
Thermodynamic Property of a CMOS Device beyond Landauer Limit
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
2024-1-23
Focusing on a CMOS NAND GATE operating in a sub-threshold region, the thermodynamic cost of computation was analyzed in relation to input/output voltages surpassing the Landauer limit.
-
Exploring Recent Advances in the Physics of Biofluid Locomotion
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Electromagnetism, optics, acoustics, heat transfer, and classical and fluid mechanics
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Mathematical methods, classical and quantum physics, relativity, gravitation, numerical simulation, computational modeling
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2023-12-8
This Special Topics Edition of the JPSJ describes the latest advances in the field of biofluid locomotion, shedding light on the underlying physics behind the movement of organisms that swim and fly.
-
Highly Accurate Estimation of Beta Decay Rates for Heavy Nuclei
Nuclear physics
2023-11-7
Physicists from Japan present complete formulas that consider the induced current and velocity-dependent terms for estimating the beta decay rates in heavy nuclei with high accuracy.
-
Discovering a Local Fluctuation Theorem with Machine Learning
Fundamental Theory of Condensed Matter Physics, Statistical Mechanics, Fluid Dynamics,
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
2023-10-20
A groundbreaking study reveals a new time-local fluctuation theorem using machine learning, revolutionizing our understanding of deterministic nonequilibrium steady state systems.
