Nanospace-confined Helium Shows Four-dimensional Quantum Phase Transition (QPT)
© The Physical Society of Japan
This article is on
Evidence for 4D XY Quantum Criticality in 4He Confined in Nanoporous Media at Finite Temperatures
(JPSJ Editors' Choice)
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 033601 (2021).
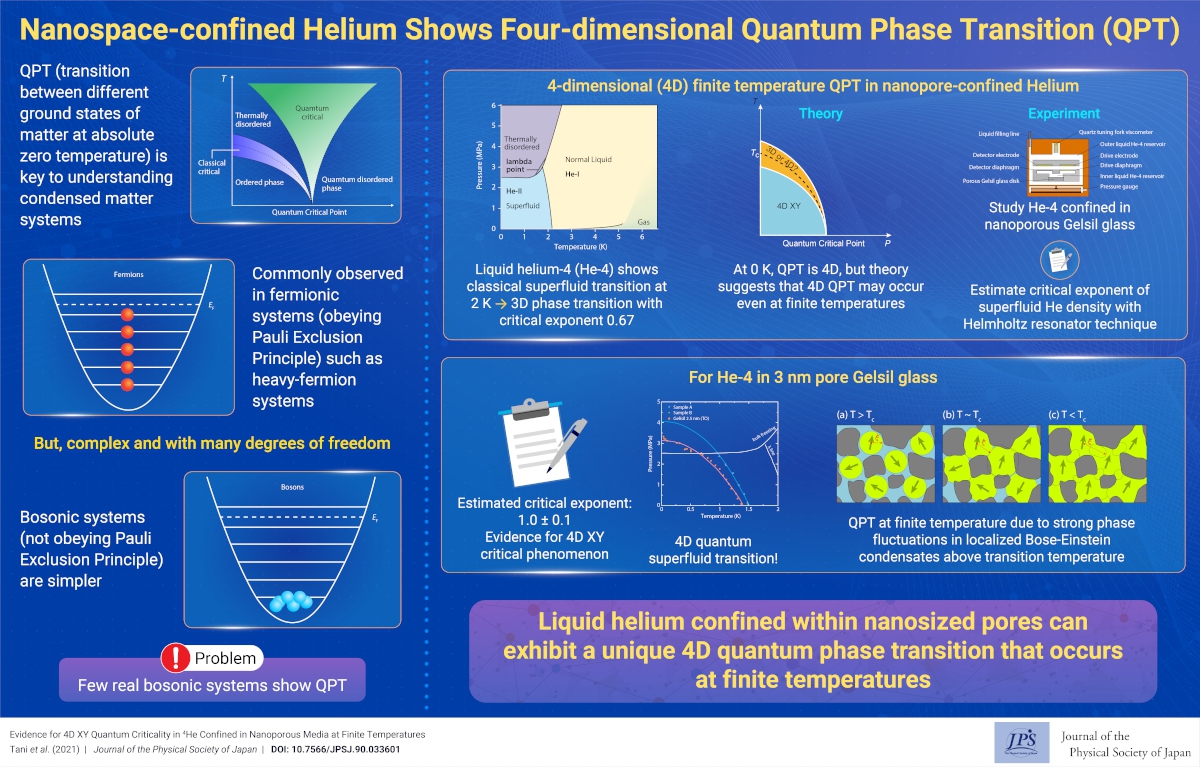
Helium confined in a nanoporous material shows a four dimensional superfluid transition. This is a unique example of four dimensional critical phenomenon caused by strong quantum fluctuation.
Evidence for 4D XY Quantum Criticality in 4He Confined in Nanoporous Media at Finite Temperatures
(JPSJ Editors' Choice)
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 033601 (2021).
Share this topic
Fields
Related Articles
-
Evaluation of the Exchange Stiffness Constants of Itinerant Magnets from the First-Principles Calculations
Electron states in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-6-5
Using first-principles calculations, we evaluated the exchange stiffness constants of ferromagnetic metals at finite temperatures. The constants can be used as parameters in the Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation.
-
Which is Moving?—Pinning Down the Origin of Fluctuations in Muon Spin Relaxation—
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
2024-3-28
The study demonstrated that we can distinguish between the diffusion motion of the muon itself and the motion of the surrounding ions in muon spin relaxation.
-
Variety of Mechanically Induced Spin Currents in Rashba Systems
Electronic transport in condensed matter
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-3-22
Various types of spin currents, including unconventional types, are generated in Rashba spin-orbit coupled systems by dynamic lattice distortions associated with, for example, surface acoustic waves.
-
Relation between Mean-Field Theory and Atomic Structures in Chalcogenide Glasses
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2024-2-1
The authors conducted various of X-ray and neutron scattering experiments on typical chalcogenide glasses and clarified the relationship between the atomic structure and simple rigidity percolation theory.
-
Possible Origin of High Thermoelectric Power Factor in Ultrathin FeSe: A Two-band Model
Electronic structure and electrical properties of surfaces and nanostructures
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
2023-12-21
The high thermoelectric power factor observed in ultrathin FeSe can be theoretically explained by a two-band model with chemical potential between upper and lower band bottoms.