Four-Dimensional XY Quantum Phase Transition in Superfluid Helium-4
© The Physical Society of Japan
This article is on
4D-XY Superfluid Transition and Dissipation in 4He Confined in Nanoporous Media
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.
91,
014603
(2022)
.
Liquid helium confined in nanopores exhibits a quantum superfluid transition at absolute zero. Investigations have revealed that the quantum nature also dominates the finite-temperature superfluid transition, obeying a simple mean-field theory.
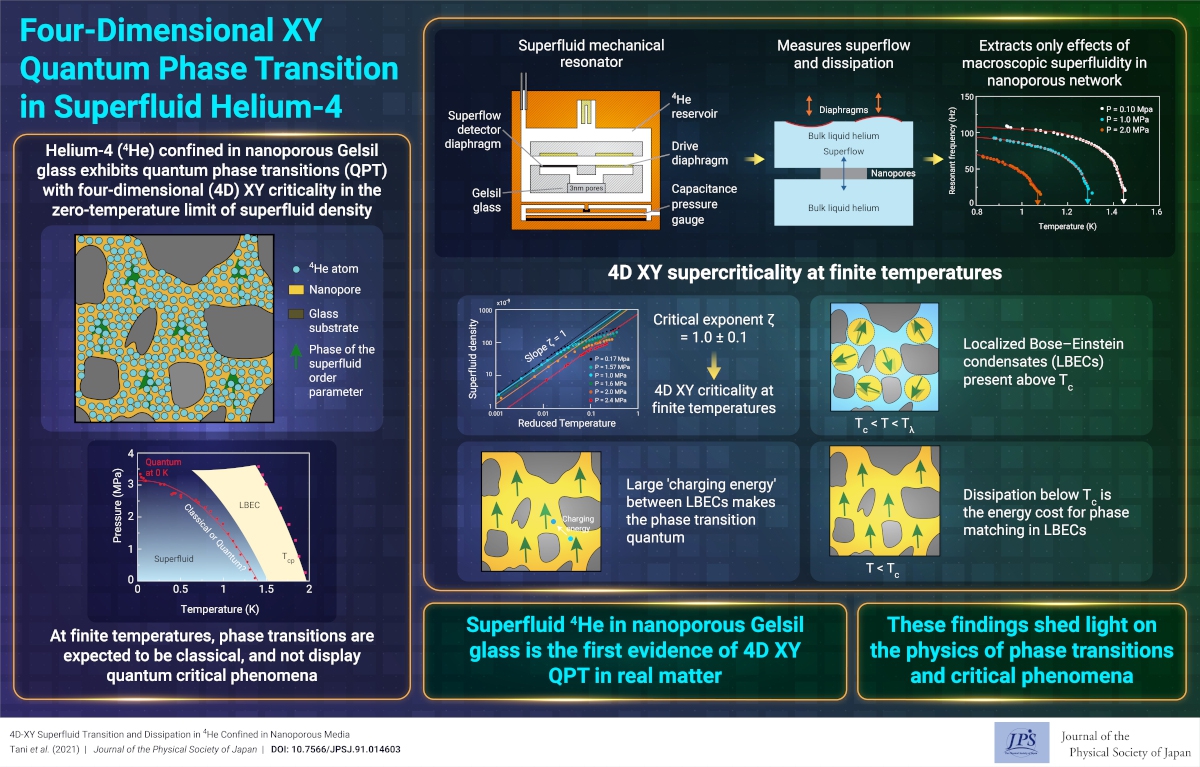
Phase transitions, such as the melting of ice, occur at finite (nonzero) temperatures as the result of thermal fluctuations, which cease as the matter is cooled to absolute zero (T = 0 K). However, even at 0 K, quantum fluctuations remain and cause another type of phase transition, called a quantum phase transition (QPT). QPT has been observed in many materials that are referred to as strongly correlated electron systems. Normally, QPT occurs only at 0 K and at a critical value of a parameter called the quantum critical point (QCP). At finite temperatures, the QCP is connected to the classical phase transition line. Therefore, QPT is believed to be unobserved at finite temperatures.
We discovered that liquid helium (4He) confined in a nanoporous material exhibits a superfluid transition governed by quantum fluctuations, even at finite temperatures. Ordinary liquid helium undergoes a phase transition from a normal viscous liquid to an extraordinary phase, called a superfluid. In the superfluid state, helium loses its viscosity, which is analogous to the zero-resistance state of superconducting electrons in metals. When liquid helium is placed into the nanopores of a porous glass called Gelsil, it exhibits a zero-temperature QPT, in which the superfluid state disappears at a certain critical pressure. However, the phase transition line in the pressure–temperature diagram exhibits a behavior that is explained by quantum criticality.
Therefore, in this work, to investigate the quantum effect at nonzero temperatures, we carefully studied the superfluid transition at many pressures using a newly developed superfluid resonator apparatus. The resonator consists of two bulk helium reservoirs separated by nanoporous glass filled with helium. When helium in the nanopores becomes a superfluid, the liquid flows between the reservoirs, resulting in a change in the resonance characteristics of the entire apparatus. We can precisely obtain the flow properties that are controlled by the superfluid density (quantity of helium atoms participating in the superfluidity) and dissipation (energy loss by nonsuperfluid components). We found that the superfluid density obeys a temperature–distance power law from the transition temperature, and the power, which is called the critical exponent, is 1.0, at all pressures measured. A critical exponent of 1 indicates that the superfluid critical phenomenon in the nanopores belongs to the four-dimensional (4D) XY universality class. This is decisive evidence for quantum criticality at finite temperatures. In ordinary bulk helium, the critical exponent is 0.67, indicating that the transition is three-dimensional.
Why is the superfluid transition of the nano-confined helium 4D? It has already been revealed that the QPT at 0 K exhibits 4D (equal to three spatial dimensions plus one imaginary time dimension) XY characteristics. At finite temperatures, superfluidity is caused by the frequent movement of helium atoms in nanopores. However, this motion was strongly suppressed at many narrow bottlenecks in the porous structure. This interruption of atom motion induces a quantum fluctuation in the superfluid order. As a result, the critical behavior changes from classical to quantum, that is, to that of a 4D XY class.
In the resonator experiment, we observed dissipation below the superfluid transition temperature. This dissipation can also be explained by its quantum nature at finite temperatures. Above the transition, helium forms many nanoscale droplets of superfluid, which are called localized Bose–Einstein condensates (LBECs). Dissipation occurs during the growth of superfluidity by matching the phases of the LBECs. The agreement of the calculated dissipation with the experimental one also establishes the validity of the quantum nature at finite temperatures.
Theoretically, the 4D transition is the simplest phase transition that can be rigorously analyzed using mean-field theory, which is the most straightforward theory describing phase transitions. Interestingly, helium in such a complicated nanoporous structure undergoes the simplest phase transition in nature. Our findings support a basic understanding of both quantum and classical phase transitions. Further studies will reveal novel superfluid phenomena governed by the quantum nature of liquid He.
(Written by K. Shirahama on behalf of all authors)
4D-XY Superfluid Transition and Dissipation in 4He Confined in Nanoporous Media
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.
91,
014603
(2022)
.
Share this topic
Fields
Related Articles
-
Qualitative Changes in Kinetic Pathways Driven by Hydrodynamic Interactions in Dense Colloidal Suspensions
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2025-4-18
Even in dense colloidal suspensions, where long-range hydrodynamic interactions are screened, near-field hydrodynamic interactions qualitatively influence the selection of kinetic pathways.
-
Bayesian Insights into X-ray Laue Oscillations: Quantitative Surface Roughness and Noise Modeling
Measurement, instrumentation, and techniques
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2025-2-14
This study adopts Bayesian inference using the replica exchange Monte Carlo method to accurately estimate thin-film properties from X-ray Laue oscillation data, enabling quantitative analysis and appropriate noise modeling.
-
Hyperuniform and Multifractal States in Bosonic Quasicrystalline Systems
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2025-2-10
Quantum states can be categorized as hyperuniform or multifractal based on electronic characteristics. This study demonstrates that bosonic quasicrystalline systems exhibit hyperuniform or multifractal quantum states.
-
Spin-Spin Interaction Mediated by Rotational Lattice Vibrations
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2025-1-24
This study predicts the presence of spin-spin interactions mediated by the angular momentum of lattice vibrations, which can be long-range.
-
Unlocking Secrets of Novel Charge-Orbital States in Transition-Metal Compounds
Cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology
Electron states in condensed matter
Electronic structure and electrical properties of surfaces and nanostructures
Magnetic properties in condensed matter
Structure and mechanical and thermal properties in condensed matter
2025-1-6
A new Special Topics edition of the Journal of the Physical Society of Japan features articles exploring special transition-metal compounds that exhibit novel charge-orbital states.




